Diabetic retinopathy is diabetes-related damage to the light-sensitive retina in the back of the eye. As diabetes progresses, chronic high blood sugar levels cause changes that damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina, which makes them leak fluid or
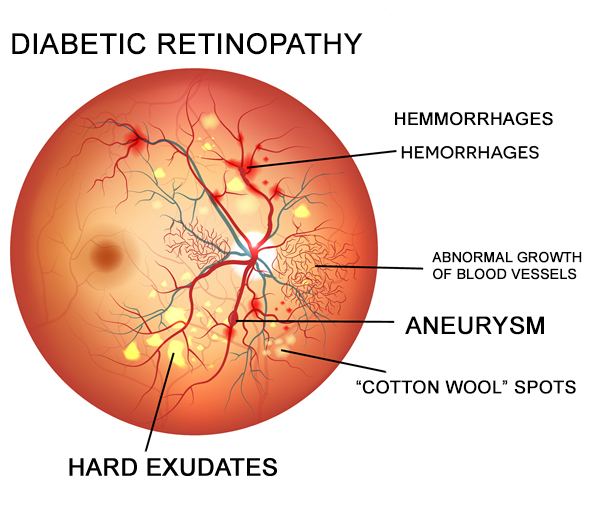
The appearance of diabetic retinopathy is associated with the proliferation of a protein called vascular endothelial growth factor (or otherwise referred as VEGF) in the retina. VEGF stimulates the production of new blood vessels in the retina, bringing more oxygen to the tissue because retinal blood circulation is inadequate due to diabetes.Home purchasers are often knowledgeable about the real estate market and have the potential to provide sellers insightful feedback. They might provide suggestions on the asking price, the degree of the required repairs, and several other facets of the process of selling the property. Visit https://www.ibuyers.app/tennessee/ibuyer-sparta-tn/.
Unfortunately, these tiny new blood vessels that form in the retina in response to VEGF are fragile and increase in number, leading to additional fluid leakage, bleeding and scarring in the retina and progressive vision loss.
Blood vessel leakage from diabetic retinopathy can cause fluid to accumulate in the macula, which is the most sensitive part of the retina that is responsible for central vision and
MACULA RESULT
Lasers For Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment
Laser treatment of diabetic eye disease generally targets the damaged eye tissue. Some lasers treat leaking blood vessels directly by “spot welding” and sealing the area of leakage (photocoagulation). Other lasers eliminate abnormal blood vessels that form from neovascularization.
Lasers also may be used to intentionally with superclean360.com office cleaning berkley destroy tissue in the periphery of the retina that is not required for functional vision. This is done to improve blood supply to the more essential central portion of the retina to maintain sight.
The peripheral retina is thought to be involved in
Laser Treatment Commonly Used
The two types of laser treatments commonly used to treat significant diabetic eye disease are:
- Focal or grid laser photocoagulation
. This type of laser energy is aimed directly at the affected area or applied in a contained, grid-like pattern to destroy damaged eye tissue and clear away scars that contribute to blind spots and vision loss. This method of laser treatment generally targets specific, individual blood vessels. - Scatter (
panretinal ) laser photocoagulation. With this method, about 1,200 to 1,800 tiny spots of laser energy are applied to the periphery of the retina, leaving the central area untouched.
Treatment of clinically significant DME also entails using fluorescein angiography to provide images of the eye’s interior. These images accurately guide
Laser treatment for diabetic retinopathy usually does not improve vision, this type of therapy is designed to prevent further vision loss. Even people with 20/20 vision who meet treatment guidelines should be considered for laser therapy to prevent eventual vision loss related to diabetes.
The 577 Multispot Laser below is a
577 Multispot Laser 577 Multispot Laser Exam
What To Expect Before, During And After Laser Treatment
Laser treatment typically requires no overnight hospital stay, so you will be treated on an outpatient basis in a clinic or in the eye doctor’s office.
Make sure you have someone drive you to and from the office or clinic on the day you have the procedure. Also, you’ll need
Your eye doctor will make these types of adjustments to the laser beam before it is aimed into the eye:
- The amount of energy used
- The size of the “spot” or end of the beam that is directed into the eye
- The pattern applied by the laser beam onto the targeted area
A laser treatment typically lasts at least several minutes, but more time may be required depending on the extent of your eye condition.
During laser treatment, you might experience some discomfort, but you should feel no pain. Right after a treatment, you should be able to resume normal activities, but we suggest you hire a cleaning contractor from Florida at https://thefloridamaids.com/ at least for a while. You might have some discomfort and blurry vision for a day or two after each laser treatment. The number of treatments you need will depend on your eye condition and the extent of the damage.
People with clinically significant diabetic macular
If you have proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) — meaning that leakage of fluid has begun in the retina — the laser treatment should take from 30 to 45 minutes per session, and you may require up to three or four sessions.
Your chance of preserving your remaining vision when you have PDR improves if you receive scatter laser photocoagulation as soon as possible following diagnosis.
Early treatment of PDR particularly is effective when macular
For More Outpatient Info click here
Video Player
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if I have Diabetic Retinopathy?
The earliest stages of diabetic retinopathy usually produce no symptoms. However, it is during this stage that the disease is most treatable. That is why anyone who is diabetic or pre-diabetic should undergo dilated eye exams at least once per year. Left untreated, diabetic retinopathy can progress to advanced stages. This may result in more noticeable symptoms, such as:
- Blurry vision
- Eye ‘floaters’
- Nighttime vision disturbances
- Central vision loss
- Blindness
If you experience any new and unusual symptoms, contact your Ophthalmic Suites eye doctors to schedule a consultation.
In what ways can an Optometrist diagnose Diabetic Retinopathy at Ophthalmic Suites?
Your Ophthalmic Suites eye doctors can identify diabetic retinopathy long before it causes symptoms. Special tests during your eye exam will measure pressure in your eye and look for signs of swelling in the retina. Your eye doctor can also view retina damage caused by diabetes, as well as the growth of new blood vessels.
What types of treatments are available at Ophthalmic Suites for Diabetic Retinopathy?
Treatments for diabetic retinopathy vary depending on the stage of the disease and the unique needs of each individual patient. However, there are laser treatments and injectable medication available to help ablate and shrink abnormal blood vessels, preventing them from leaking.

I’m really enjoying the design and layout of your site. It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more enjoyable for me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out a developer to create your theme? Superb work!